Health Crisis Upends Commercial Real Estate' Uncertainty Will Carry Well Into 2021
Pandemic Transforms Commercial Real Estate.
COVID-19 changed the world in early 2020 as efforts to curb the spread of the pandemic had a dramatic impact. Stay-at-home orders, the need to physically distance, and having to abide by health and safety protocols had harsh effects on many real estate sectors.
Health Crisis Exacerbated Demographic Shifts.
Employers laying off workers and sending staff home to work remotely contributed to an acceleration of demographic changes that were already underway. Economic uncertainty led many households to search for lower-cost housing, while the need to work from home and attend school online generated demand for larger spaces. Commute times became less of a factor in housing decisions, pushing residential and apartment demand away from dense urban cores that are more reliant on mass transit to the benefit of suburbs as well as secondary and tertiary markets. Higher unemployment is also leading to more people spending time at home, which consequently may have boosted new business applications to the highest rate since the Great Recession.
Possibilities for Second Growth Surge or Double Dip in 2021 Hinge on Vaccine Rollout and Labor Recovery
Vaccine distribution to play a critical role in economic outlook.
The nation's economic situation has regained much of the momentum lost last spring as it continues along an upward path in 2021. Ongoing health challenges and other potential hurdles may suspend or abate that progress, however. If the current set of COVID-19 vaccines are distributed as efficiently as predicted, then enough people may be inoculated by midyear to safely allow most businesses to fully reopen. If, however, the pace of the vaccine rollout is slowed or the nature of the virus changes, these exogenous encumbrances to the economy will remain in place longer. Employers who are challenged by physical distancing requirements and areas of the country where infection risk is higher will fall further behind other segments of the economy. This disparity, if severe enough, could lead to another quarterly economic contraction.
Labor market recovering but some sectors are falling behind.
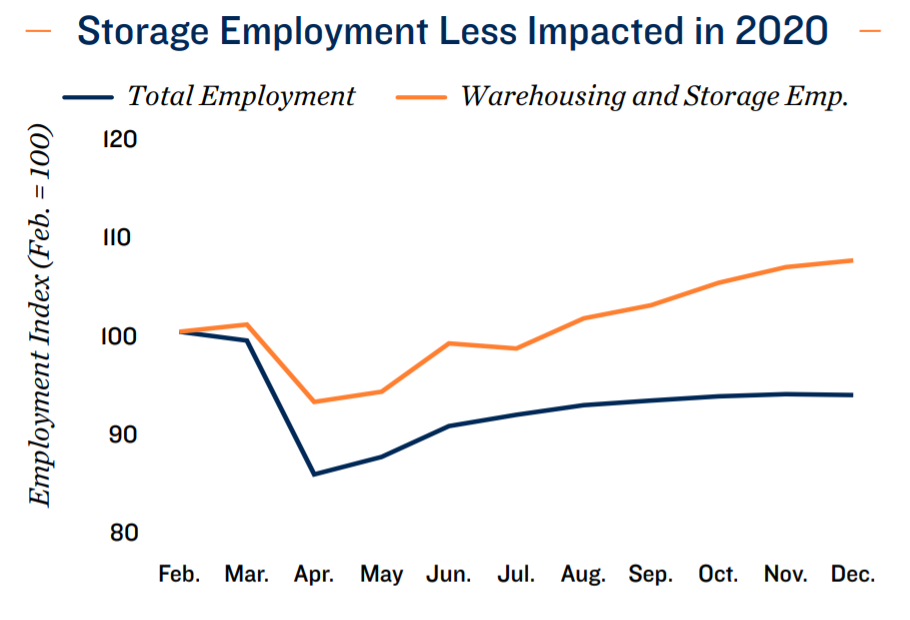
Over half of the jobs lost in March and April last year were restored or replaced by December, but as 2021 progresses certain industries face a longer road to total recovery than others. Physical distancing requirements and travel restrictions had a disproportionate impact on the leisure and hospitality sector, which encompasses hotels, bars, restaurants and other entertainment venues. While the overall employment base remained 6.5 percent below its pre-pandemic level at the start of 2021, the leisure and hospitality sector was still down 23.2 percent. Conversely, staff working in essential services or in positions more easily shifted to a remote setting were better protected. The number of jobs in financial activities, construction and in the trade, transportation and warehousing sector were all at or within 3 percent of their February 2020 mark by the start of the new year.
Administration Weighs Policy Goals Against Stimulus Needs While the Federal Reserve Guides Inflation
Biden administration must balance policy objectives and health crisis management.
President Biden campaigned on a platform of widespread legislative reform, including taxation, healthcare and public spending on infrastructure. Achieving these goals must be managed in relation to the immediate needs of the health crisis. Making more substantial alterations to laws and regulations could create uncertainty among consumers and investors, dampening the intended effects of stimulus measures that the Biden administration is currently pursuing.
Additional federal aid likely incoming; holds significant implications on growth.
The $900 billion stimulus package passed at the end of last year is serving as a vital economic stopgap as the country deals with the difficult health challenges. Many of the legislation's key benefits, such as renewed federal unemployment insurance, will nevertheless fade by the spring. The Biden administration is therefore pursuing a $1.9 trillion stimulus package to further buttress the economy. While the final stipulations of the bill are almost certain to change, the incoming aid will uplift the economy in the near term, but at the cost of introducing some potential longer-term risks.
The Federal Reserve continues to carefully monitor inflation.
As this year progresses, the Fed will have to walk a tightrope balancing economic growth and the potential for accelerated inflation.
Resilient Self-Storage Sector Emerges From 2020 on Upward Path, Aided by Historically Strong Fundamentals
Initial uncertainty briefly weighed on self-storage performance.
When a wave of stay-athome orders came into effect in March 2020 in response to the health threats of COVID-19, many commercial real estate demand factors were substantially disrupted. Self-storage properties were not immune to this trend. While storage was classified as essential business and permitted to stay open during lockdown, general uncertainty about the health situation kept many renters away from their units. Although more people sequestering at home means that fewer tenants were ending existing leases, fewer new rental agreements were also being signed.
Sector recovers in the second half of 2020, achieving new vacancy low.
As spring moved into summer and the impact of the pandemic became more clear, the self-storage sector began to demonstrate its resilience. New leasing improved as stay-at-home orders were relaxed and customers felt more comfortable visiting units. At the same time more existing tenants were holding onto their units for longer, even after many eviction moratoriums ended.
Transaction environment improves from early disruption.
The investment landscape for self-storage properties mirrored the operational changes of the sector in many respects. During the initial period of uncertainty, sales velocity slowed, both due to logistical limitations in closing trades as well as ambiguity over cash flows. As property performance stabilized and then improved, transaction activity similarly rebounded, with buyer competition adding upward pressure to the average sales price. Trading volume and pricing are well above previous economic cycles, even with current challenges, and the tight competition for assets is anticipated to continue.
Outlook for 2021 points to continued growth.
As a new year progresses, the self-storage sector is poised to ride several demand tailwinds. Remote learning and working are taking away storage space in the home, while businesses also must put aside excess items amid physical distancing.